Have you seen SmartWindows with adjustable transparencies before? To make them more ubiquitous, a research team proposed a more comprehensive strategy to evaluate their effectiveness, considering energy, environmental and personnel comfort.
Summary
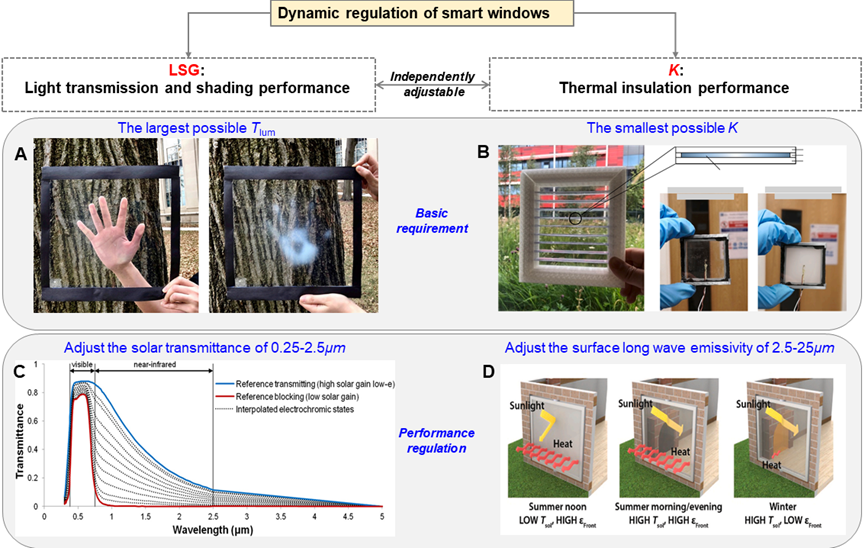
Thermochromic and electrochromic smart windows are increasingly receiving attention for their specific ability to regulate the dynamics of light and heat. The goal of improving smart-window materials is chiefly to achieve building applications. This paper reviews the progress of existing material technologies and summarizes their experiments and simulations related to buildings. To facilitate the leap from material to building, the concept of performance regulation of ideal smart windows is proposed, and the applicability distribution of existing technologies is mapped. Based on the completely different core logic of thermochromic and electrochromic smart windows, the discrepancies and consistencies between the two are discussed. Performance requirements of smart windows in materials and buildings are proposed. Bridging the gap between materials and buildings for interdisciplinary promotion is the key to further exploration of the potential application of smart windows and accelerating their applications in the future.